EFPRA's members produce a wide range of rendered by-products that become the raw materials in all sorts of industries. Safer material often re-enters the food chain while category 1 by-products are a lower carbon-footprint replacement for fossil fuels. The diagram below shows the main uses of rendered products:
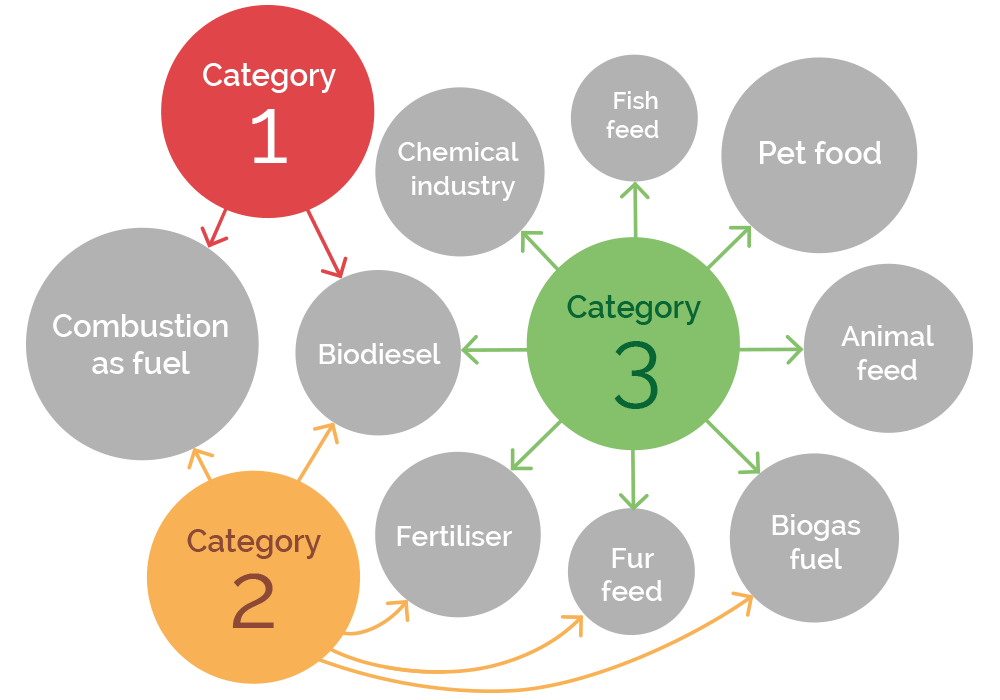

Combustion as fuel
Solid fuel for power stations and cement kilns - equivalent to 1 million tonnes of coal but with a much lower carbon footprint.

Biodiesel
Rendered fat is blended into the diesel sold at fuel stations across the EU
Pet food
PAP is a key component of dry pet foods and is a substitute for vegetable proteins like soya beans which we import from outside the EU.
Aquafeed
PAP is an ingredient of aquafeed - particularly for commercially grown carnivorous fish like salmon. PAP has better nutritional properties than vegetable proteins for fish and can also substitute for wild-caught fish in feed rations.

Chemical industry
Rendered fat is the raw material for oleochemicals (fats and lipids). We use these as ingredients for a range of household good such as cosmetics, lubricants and cleaning products.

Animal feed
Processed Animal Protein can form part of thefeed rations of omnivorous and carnivorous animals - as long as there is no intra-species consumption. Category 3 fat is a feed ingredient because of its binding, preservative and nutritional properties.

Fertiliser
Animal by-products make fertiliser that is rich in phosphorous - a vital element for plant growth and photosynthesis, it contains good quantities of nitrogen and various micro-nutrients.

Biogas
This fuel can substitute for fossil gas used for heating and electricity generation.
Edible by-products
Many EFPRA members also produce edible products - particularly fat and also greaves - the raw material for these products is separated at the abattoir and is always managed as food rather than Category 3 by-product. Find out more on the edible fats page »
